| . |  |
. |
Washington DC (SPX) Dec 21, 2010 With frigid temperatures already blanketing much of the United States, the arrival of the winter solstice on December 21 may not be an occasion many people feel like celebrating. But a dazzling total lunar eclipse to start the day might just raise a few chilled spirits. Early in the morning on December 21 a total lunar eclipse will be visible to sky watchers across North America (for observers in western states the eclipse actually begins late in the evening of December 20), Greenland and Iceland. Viewers in Western Europe will be able to see the beginning stages of the eclipse before moonset, and in western Asia the later stages of the eclipse will be visible after moonrise. From beginning to end, the eclipse will last about three hours and twenty-eight minutes. For observers on the east coast of the U.S. the eclipse lasts from 1:33am EST through 5:01 a.m. EST. Viewers on the west coast will be able to tune in a bit earlier. For them the eclipse begins at 10:33 p.m. PST on December 20 and lasts until 2:01am PST on Dec. 21. Totality, the time when Earth's shadow completely covers the moon, will last a lengthy 72 minutes. While it is merely a coincidence that the eclipse falls on the same date as this year's winter solstice, for eclipse watchers this means that the moon will appear very high in the night sky, as the solstice marks the time when the Earth's axial tilt is farthest away from the sun. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth lines up directly between the sun and the moon, blocking the sun's rays and casting a shadow on the moon. As the moon moves deeper and deeper into the Earth's shadow, the moon changes color before your very eyes, turning from gray to an orange or deep shade of red. The moon takes on this new color because indirect sunlight is still able to pass through Earth's atmosphere and cast a glow on the moon. Our atmosphere filters out most of the blue colored light, leaving the red and orange hues that we see during a lunar eclipse. Extra particles in the atmosphere, from say a recent volcanic eruption, will cause the moon to appear a darker shade of red. Unlike solar eclipses, lunar eclipses are perfectly safe to view without any special glasses or equipment. All you need is you own two eyes. So take this opportunity to stay up late and watch this stunning celestial phenomenon high in the night sky. It will be the last chance for sky watchers in the continental U.S. to see a total lunar eclipse until April 15, 2014.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links NASA Mr. Eclipse web site NASA Watch the Skies web site Solar and Lunar Eclipses at Skynightly
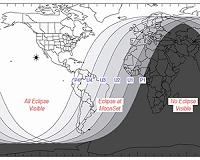 Solstice Lunar Eclipse
Solstice Lunar EclipseHuntsville AL (SPX) Dec 20, 2010 Everyone knows that "the moon on the breast of new-fallen snow gives the luster of mid-day to objects below." That is, except during a lunar eclipse. The luster will be a bit "off" on Dec. 21st, the first day of northern winter, when the full Moon passes almost dead-center through Earth's shadow. For 72 minutes of eerie totality, an amber light will play across the snows of North America ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |