| . |  |
. |
Pasadena - Nov 19, 2003 Some climate forecast models indicate there is an above average chance that there could be a weak to borderline El Ni�o by the end of November 2003. However, the trade winds, blowing from east to west across the equatorial Pacific Ocean, remain strong. Thus, there remains some uncertainty among climate scientists as to whether the warm temperature anomaly will form again this year. The latest remote sensing data from NASA's Jason satellite show near normal conditions across the equatorial Pacific. There are currently no visible signs in sea surface height of an impending El Ni�o. This equatorial quiet contrasts with the Bering Sea, Gulf of Alaska and U.S. West Coast where lower-than-normal sea surface levels and cool ocean temperatures continue (indicated by blue and purple areas). The image above is a global map of sea surface height, accurate to within 30 millimeters. The image represents data collected and composited over a 10-day period, ending on Nov. 3, 2003. The height of the water relates to the temperature of the water. As the ocean warms, its level rises; and as it cools, its level falls. Yellow and red areas indicate where the waters are relatively warmer and have expanded above sea level, green indicates near normal sea level, and blue and purple areas show where the waters are relatively colder and the surface is lower than sea level. The blue areas are between 5 and 13 centimeters (2 and 5 inches) below normal, whereas the purple areas range from 14 to 18 centimeters (6 to 7 inches) below normal. The Jason satellite carries a dual-frequency radar altimeter. This instrument beam microwave pulses-at 13.6 and 5.3 Gigahertz, respectively-downward toward the Earth. To determine the ocean's height, the instrument precisely measures the time it takes for the microwave pulses to bounce off the surface and return to the spacecraft. This measure, multiplied by the speed of light, gives the range from the satellite to the ocean surface. (For more details, visit the Jason Website.) Related Links Elnino at JPL SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 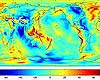 Boston - Nov 19, 2003
Boston - Nov 19, 2003Back in the old days, when doctors looked for tumors, exploratory surgery was the only option. Today they use CAT scans, x-rays, ultrasound, and other non-intrusive methods for checking out what lies beneath the skin's surface. But how do we determine what is beneath the Earth's surface? Invasive surgery on the Earth is just as dated as doctors' old methods of finding tumors, if you ask Eric Miller, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at Northeastern University. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |