| . |  |
. |
Moffett Field CA (SPX) Oct 28, 2004 Imagine an oil drum the size of a school bus with an antenna on top. That description paraphrases how Cassini points mechanically at Saturn and its moons. During Cassini's most complex maneuvers so far, nearly a dozen scientific instruments moved rigidly as the spacecraft shifted its orientation. When pointing a particular instrument, the entire probe must rotate. All the cameras, radar and even an atmospheric scoop remained stationery Wednesday morning as Cassini pirouetted around Saturn's largest moon, Titan. What is so impressive about Cassini is its varied suite of instruments, each focused and designed for a different investigation. Like piecing together a three-dimensional puzzle, the goal is to fit each data set into a consistent view. Some initial impressions were garnered from a 32 hour maneuver only 700 miles above Titan. The flyby was close enough to scoop up a sample of the moon's thick atmosphere. There were three questions the flyby aimed to clarify. Why does Titan have an atmosphere at all? What is methane's role in that atmosphere? Does this methane supply liquid lakes or even oceans on the surface? The visual impressions of Titan reached resolutions 100 times better than previous views. The best pictures could resolve an area about the size of a few football fields. Standing out from the initial flyby was the ten to twenty percent contrast between dark and light areas. Titan has a complex visual texture. Does this glowing orange pumpkin have veins? There seems to be a directionality or streakiness to some of the bright areas. This may support a wind-driven explanation for what may be happening as fine dust is blown preferentially from relative northwest to southeast. An alternative view of this is that fractures or seismic features may dominate the linear streaks shown in early, unprocessed images. Because Titan is large - the second largest moon in the solar system - its rocky composition has plenty of subterranean energy from heavier elements like uranium. This energy - whether tectonic or seismic - may play an active role. What is most striking about Titan is its lack of impact craters. The cratered face so familiar on our own moon may be masked on Titan by near-surface clouds or resurfaced by methane glaciers. The relative smoothness of Titan interests scientists as evidence of the moon's changing face. One hypothesis to test is whether the dark areas are liquid. The forthcoming Huygens descent to Titan's surface might dramatically splashdown after Christmas. Other than Earth, Titan is perhaps the only place in our solar system where a probe might announce its arrival with a big splash. One could hope that such close investigations could zero in on the darkest spot on Titan, then point the descending Huygens probe to target exactly that place. In practice, the landing site for Huygens is governed less by such scientific curiousity and more by engineering constraints. Titan is a tough target to land on. During Huygens' descent in a few months, the light and angles will have to be just right. The probe will send back its best pictures if the Sun-Cassini-probe angle remains high, meaning that overall illumination is good. To measure wind speed and drift as the Huygens' parachute descends, the entry also needs to be slightly off the equator. These engineering contraints have limited the probable landing ellipse to a complex region of bright and dark albedo. The target is not only dark, as one might hope. But if scientists get their wish, this destination will still resemble a shoreline or actually place the probe on top of a liquid hydrocarbon ocean. From the mission control room, the call Wednesday morning echoed hopes for just such 'a beachfront landing'. While the images tell one story, the radar instruments may help answer the immediate question: is there liquid on Titan? Radar wavelengths can resolve textures about the size of a human hand. While a solid surface may show roughness at this dimension, a pooling liquid with little surface wind will reflect like glass when the radar image is processed. When viewed by radar, one tell-tale sign of liquid on Titan may come later Wednesday if a dark area appears reflective and smooth. Scientists conclude so far that there are lots of features, and also that Titan is a tough target. Whether the light-dark boundaries show elevation or depression will be answerable once a stereo camera gets a three-dimensional perspective on any discernable shadows. Understanding these pictures depends on meshing as many instrument views as possible. This 'complete body scan' integrates visual, infrared and ultraviolet photos. It combines radar with an actual atmospheric scoop of what is thought to be methane, smog or aerosols. This thick soup may be stirred by Saturn's magnetic field, methane rain, frigid winds and even surface tectonics. During the Cassini encounter with Titan, all these strategies will be evolved stepwise to get ever closer views. When the mission began, radar was the only remote tool that was guaranteed to penetrate Titan's thick clouds. But as the mission has taken shape, it has become increasingly clear that visual instruments will also contribute to answering the main questions that Titan poses. The most specialized Cassini scientist still looks at images to interpret their numbers-even at such great distances from Earth, seeing is believing. At first glance, the most surprising 'instant science' is the directionality or streakiness of surface features. These trails may indicate the thick atmosphere's effects on Titan's surface. Is this scouring? Does this pattern show winds blowing fine dust, as winds also shape the surface detail on Mars? During the mission life, over forty close encounters with Titan are planned. Titan is likely our solar system's greatest unexplored territory, particularly if this glowing orange dot turns out to resemble the primordial Earth. Related Links Cassini at JPL Cassini Image Team SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express 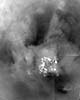 Washington (UPI) Oct 28, 2004
Washington (UPI) Oct 28, 2004NASA's Cassini spacecraft just flew closer to Saturn's giant moon Titan than any other device built by humans. The mission, in one of the far corners of the solar system, is attempting to answer a very large, critical question - does life exist anywhere else in the universe? |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |