| . |  |
. |
Austin, TX (SPX) May 20, 2011 An essential component of animal nervous systems-sodium channels-evolved prior to the evolution of those systems, researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have discovered. "The first nervous systems appeared in jellyfish-like animals six hundred million years ago or so," says Harold Zakon, professor of neurobiology, "and it was thought that sodium channels evolved around that time. We have now discovered that sodium channels were around well before nervous systems evolved." Zakon and his coauthors, Professor David Hillis and graduate student Benjamin Liebeskind, published their findings this week in PNAS. Nervous systems and their component neuron cells were a key innovation in the evolution of animals, allowing for communication across vast distances between cells in the body and leading to sensory perception, behavior and the evolution of complex animal brains. Sodium channels are an integral part of a neuron's complex machinery. The channels are like floodgates lodged throughout a neuron's levee-like cellular membrane. When the channels open, sodium floods through the membrane into the neuron, and this generates nerve impulses. Zakon, Hillis and Liebeskind discovered the genes for such sodium channels hiding within an organism that isn't even made of multiple cells, much less any neurons. The single-celled organism is a choanoflagellate, and it is distantly related to multi-cellular animals such as jellyfish and humans. The researchers then constructed evolutionary trees, or phylogenies, showing the relationship of those genes in the single-celled choanoflagellate to multi-cellular animals, including jellyfish, sponges, flies and humans. Because the sodium channel genes were found in choanoflagellates, the scientists propose that the genes originated not only before the advent of the nervous system, but even before the evolution of multicellularity itself. "These genes were then co-opted by the nervous systems evolving in multi-cellular animals," says Hillis, the Alfred W. Roark Centennial Professor in Natural Sciences. "This study shows how complex traits, such as the nervous system, can evolve gradually, often from parts that evolved for other purposes." "Evolutionarily novel organs do not spring up from nowhere," adds Zakon, "but from pre-existing genes that were likely doing something else previously." Liebeskind, a graduate student in the university's ecology, evolution and behavior program, is directing his next research efforts toward understanding what the sodium channels do in choanoflagellates.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links University of Texas at Austin Explore The Early Earth at TerraDaily.com
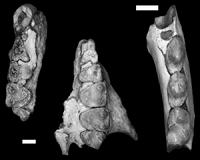 Anthropologist discovers new fossil primate species in West Texas
Anthropologist discovers new fossil primate species in West TexasAustin TX (SPX) May 18, 2011 Physical anthropologist Chris Kirk has announced the discovery of a previously unknown species of fossil primate, Mescalerolemur horneri, in the Devil's Graveyard badlands of West Texas. Mescalerolemur lived during the Eocene Epoch about 43 million years ago, and would have most closely resembled a small present-day lemur. Mescalerolemur is a member of an extinct primate group - the adapif ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |