| . |  |
. |
London, UK (SPX) Jan 15, 2008 Recognising people, objects or animals by the sound they make is an important survival skill and something most of us take for granted. But very similar objects can physically make very dissimilar sounds and we are able to pick up subtle clues about the identity and source of the sound. Scientists funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) are working out how the human ear and the brain come together to help us understand our acoustic environment. They have found that the part of the brain that deals with sound, the auditory cortex, is adapted in each individual and tuned to the world around us. We learn throughout our lives how to localise and identify different sounds. It means that if you could hear the world through someone else's ears it would sound very different to what you are used to. The research, which features in the current issue of BBSRC Business, could help to develop more sophisticated hearing aids and more effective speech recognition systems. The research team at the University of Oxford, led by Dr Jan Schnupp, have studied the auditory cortex of the brain and discovered that its responses are determined not merely by acoustical properties, like frequency and pitch, but by statistical properties of the sound-scape. In the world loudness and pitch are constantly changing. The random shifts in sounds are underpinned with a statistical regularity. For example, subtle and gradual changes are statistically more regular than large and sudden changes. Dr Schnupp's team have found that our brains are adapted to the former; the neurons in the auditory cortex appear to anticipate and respond best to gradual changes in the soundscape. These are also the patterns most commonly found in both nature and musical compositions. Dr Schnupp, a research leader at the University of Oxford Auditory Neuroscience Group, said: "Our research to model speech sounds in the lab has shown that auditory neurons in the brain are adaptable and we learn how to locate and identify sounds. Each person's auditory cortex in their brain is adapted to way their ears deliver sound to them and their experience of the world. If you could borrow someone else's ears you would have real difficulty in locating the source of sounds, at least until your brain had relearned how to do it." Dr Schnupp has also found that the auditory cortex does not have neurons sensitive to different aspects of sound. When the researchers look at how the auditory cortex responds to changes in pitch, timbre and frequency they saw that most neurons reacted to each change. Dr Schnupp explains: "In the closely related visual cortex there are different neurons for processing colour, form and motion. In the auditory cortex the neurons seem to overwhelmingly react to several of the different properties of sound. We are now investigating how they distinguish between pitch, spatial location and timbre. "If we can understand how the auditory cortex has evolved to do this we may be able to apply the knowledge to develop hearing aids that can blot out background noise and speech recognition systems that can handle different accents." The Oxford team's current project is using BBSRC funding to fit trained ferrets with harmless auditory implants. The animals are trained to respond to different sounds and the implants enable the team to observe the auditory neurons as the ferret responds to different sounds. Professor Nigel Brown, BBSRC Director of Science and Technology, said: "This research is revealing how our senses work and how the brain interprets Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council All About Human Beings and How We Got To Be Here
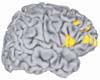 Cambridge MA (SPX) Jan 14, 2008
Cambridge MA (SPX) Jan 14, 2008People from different cultures use their brains differently to solve the same visual perceptual tasks, MIT researchers and colleagues report in the first brain imaging study of its kind. Psychological research has established that American culture, which values the individual, emphasizes the independence of objects from their contexts, while East Asian societies emphasize the collective and the contextual interdependence of objects. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |