| . |  |
. |
Beijing (AFP) July 30, 2007 China's environment watchdog said Monday it will make it harder for heavily energy-consuming, highly polluting industries to borrow money from the banks. The State Environmental Protection Administration will regularly hand over lists of violators of environmental rules to the central bank and the China Banking Regulatory Commission, the administration said on its website. Banks must conduct strict investigations into loans to proposed projects based on the information and are forbidden from extending any credit to new projects that have not undergone proper environmental assessments, it said. A blacklist of 30 companies, including paper makers, copper plants, steel firms, pharmaceutical manufacturers and breweries, has already been submitted to lenders across the country, said Pan Yue, the administration's deputy head. Increasing the funding costs for heavy industries and even cutting off sources of credit for those companies that seriously violate the laws, have become an urgent matter for curbing their investment momentum, he added. China has set goals of reducing energy consumption per unit of gross domestic product by 20 percent and cutting emissions of pollutants by 10 percent from levels in 2005 by 2010. However, the job looks to be an increasingly tough one as high energy-consuming firms grew by 20.1 percent in the first half of the year after emission of air and water pollutants actually rose by two percent in 2006.
Source: Agence France-Presse Community Email This Article Comment On This Article Related Links Our Polluted World and Cleaning It Up
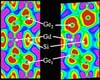 Argonne Il (SPX) Jun 20, 2007
Argonne Il (SPX) Jun 20, 2007Materials that change temperature in magnetic fields could lead to new refrigeration technologies that reduce the use of greenhouse gases, thanks to new research at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory and Ames National Laboratory. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |